Chemistry
Molecular Potential Energy Surfaces: Application to Atmospheric, Interstellar and Combustion Chemistry
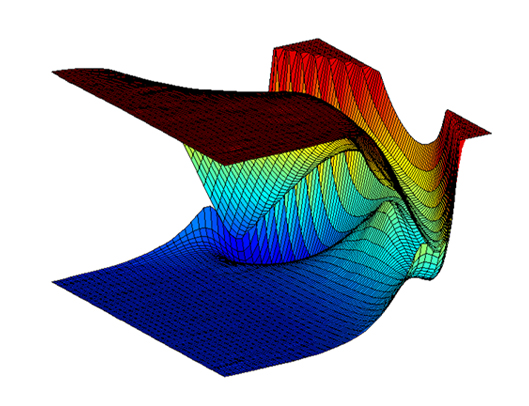
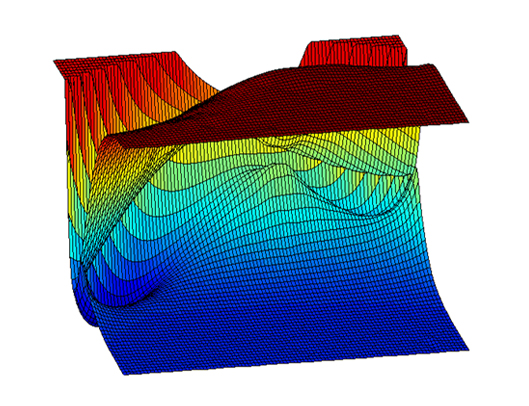
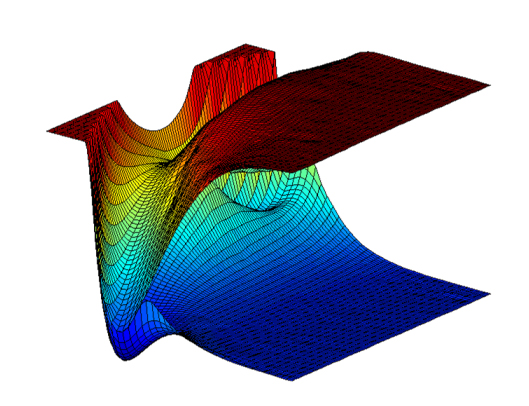
-Interacting potential energy surfaces in the HCO molecule-
The Born-Oppenheimer molecular potential energy surface (PES) is central to how chemists think about the structure and dynamics of molecular systems, ranging from equilibrium structures at minima to product-channel asymptotes, connected by paths across landscapes and over energetic barriers. In this framework, the potential for the nuclei is obtained by connecting electronic energies at a series of discrete nuclear positions (geometries) into a surface. PESs are the essential starting point for nearly all calculations of quantum states, properties, and dynamics of molecules making them the foundation of theoretical chemistry.
Principal Investigator
Richard Dawes
Associate Professor
573-341-4451 | dawesr@mst.edu |
120C Schrenk Hall
Physical chemistry, theoretical spectroscopy, molecular dynamics.
